Body in White (BIW) Benchmarking
ADAS Radar Sensor Teardown & Should Costing
Coating Benchmarking
On average, more than 50 % of parts in a vehicle are coated & based on our past experience with >30 Vehicles teardown & VA/VE exercise, we have devised a strategy to reduce the cost of coatings. We at Advanced Structures India use Engineering Intelligence to reduce the impact of coating type and thickness on the cost of commercial vehicles and passenger cars.
*All data/graphs/trends/images presented on this page are dummy/heavily masked/edited to remove specific details. They are intended only to showcase sample outcomes of such activities.
This Blog will focus on the following aspects of CVs and 4Ws:
- Potential in coating cost optimization
- Available types of coating and thickness distribution among different sub systems of vehicle
- Quantified impact of coatings on overall cost of a vehicle
- Strategy to reduce the impact of coatings on vehicles
- Example cost saving ideas with respect to coatings on vehicle
Why is there a need to optimize coatings on vehicles?

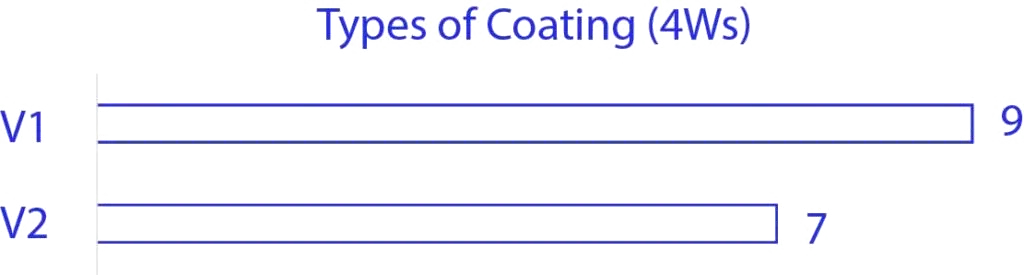
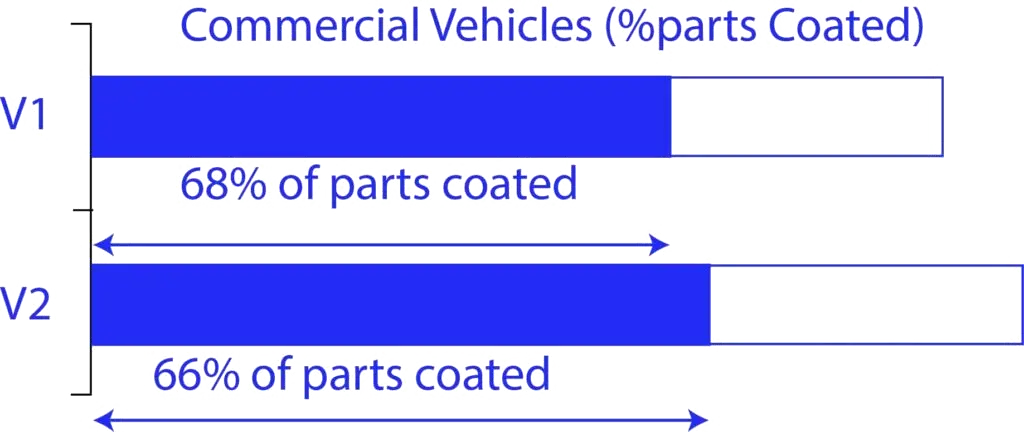
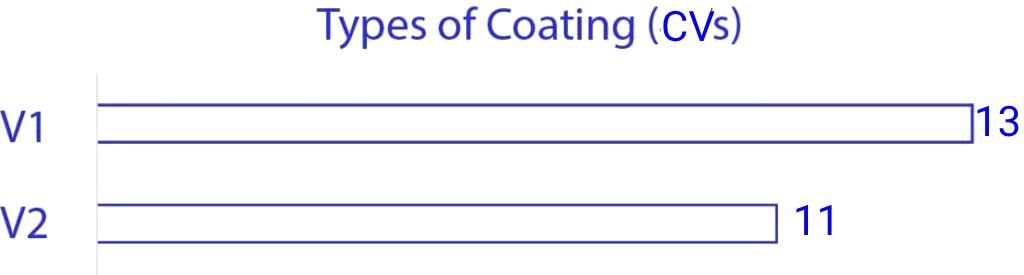
The data shown above suggests that around 50% of the parts in passenger cars are coated with 7 to 9 variety of coat types. Similarly, in commercial vehicles >65% of the parts are coated with 11 to 13 variety of coating types. We have also seen vehicles with <30% of the parts that need coatings & even the types of coatings were optimised to mainly 5 varieties. So, all the observations we had is aligned towards the possibility of a structured approach with which we can achieve great cost savings when analysing the layers applied over the material.
Available types of coating and thickness distribution
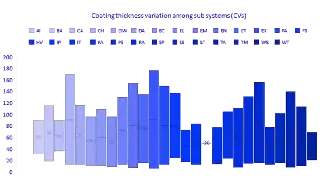
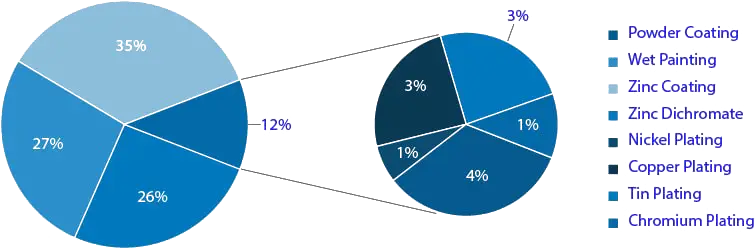
Presented below is the data from our experience of teardown of >10 trucks & >15 Passenger cars. A quick summary of types of coatings and number of parts coated compared to total in 4W & Trucks is shown below.
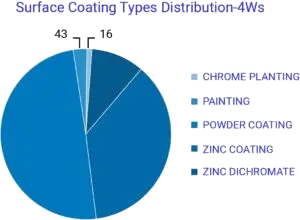
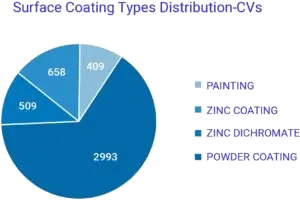
More than 50% out of total coated parts have zinc coating and zinc dicromate in vehicles (4W & CV), this is mainly fasteners. However, other than fasteners all parts have either painting or powder coating in both types of vehicles (ref. Fig. 2 and less than 3% of coated parts have other types of coating like chrome plating, phosphate coating, etc.

Fig -3
Table 1 (Sub-System Division)
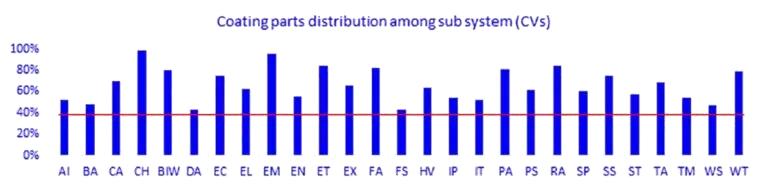
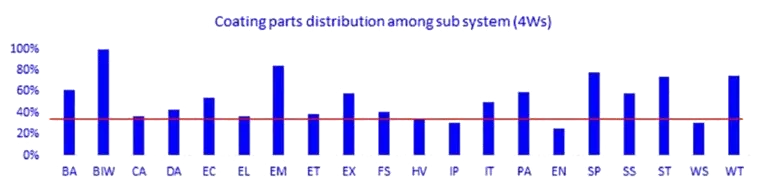
Fig -5
In 4-Wheelers among all the 20 sub-systems (ref. table 1), there are more than 30% of coated parts in each sub system and in CVs among all 28 sub-systems (ref. table 1), there are more than 50% of coated parts in each sub-system (ref. Fig 4&5). This shows that coatings have a huge coverage among all the sub-systems and huge potential lies if optimized with a structured approach.
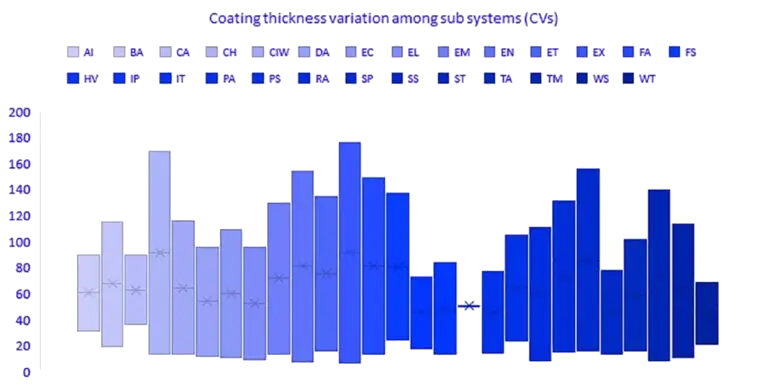
Fig -6
Quantified impact of coatings on cost of a vehicle
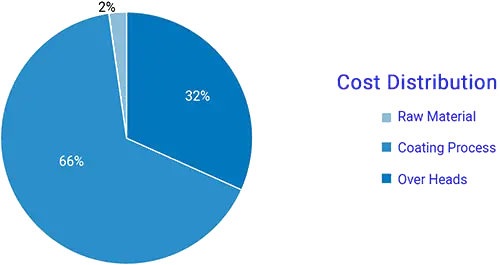
In total coating cost maximum contribution is by coating process, followed by raw material and remaining 1-2% is covered by overheads. This depicts that there is a high probability of reducing the cost by changing the coating process and also change in raw material.
How to reduce coating cost while benchmarking with competitor? (Cost Optimization Strategy)
Mainly the strategy will be followed in absolute terms on one vehicle or in comparison with competitor vehicle.
- Select the vehicle for coating study with the competitor.
- Comprehensive measurement of coating details
- Coating type (chemical composition)
- Coating thickness measurement (total thickness and layer wise thickness study)
- Coating application area and thickness distribution among the sub-systems from the BOM (ref. Fig. 8) of the vehicle
- Application study (corrosion, aesthetics & sealing etc.) of coatings on the vehicle sub system wise at different locations in the vehicle.
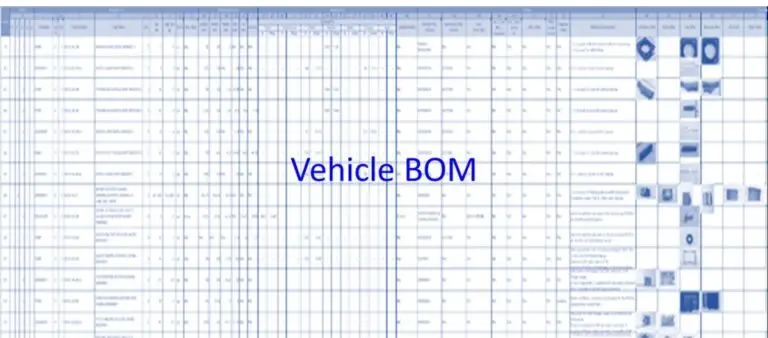
- Analysis & Potential Estimation, few methods
- Changing the type of coating - After studying the part application and function in the vehicle, we suggest to change the type of coating based on distribution, type & thickness. This results in cost saving through both raw material and coating process.
- Reducing the coating thickness - Coating thickness of each layer of part will be studied at different locations and based on its functionality and usage, we suggest to reduce the coating thickness. So that the raw material cost of coating can be saved.
- Reducing the number of layers of coating Layer wise coating analysis will be done and based on the application and usage of the part or assembly; we can reduce the number of coating layers. This results in elimination of entire single/multiple layer coating process on part.
- Changing the type of raw material used for coating After analysing the raw material used for coating, we will suggest for alternate, & economical raw material.
- Research of new coating process to reduce the cost Based on different coating techniques used for different types of parts, from our database we suggest a new cost-effective technique of coating process.
- Eliminate the coating process on part As per part functionality and its mounting location, we suggest to eliminate the coating on the part, if there is no significance of coating the part. This results in cost saving in both coating material and coating process.
Fig -9
- Generate ideas based on the data mapped automatically using our xcPEP platform where idea generation & management is done till the ideas are implemented.(53% of Ideas Implemented.)</>
- The further step is to check the feasibility of generated ideas from different aspects and implementing the ideas. From the above-mentioned methods, we have generated ideas on 4-Wheelers and 52% of the total generated ideas are implemented.
Example Cost saving ideas based on coating cost optimization strategy

Reducing the top thickness by 50 microns resulted in 7.5% of cost saving in raw material of coating



